Respiratory Protection for Lead Exposure
The employer must provide employees with the following to keep them safe!
- Respirators that comply with the requirements of exposure.
- Medical examination(s).
- The employer must train and fit test all affected employees with the appropriate respirators according to level of exposure.
- The employer must implement a respiratory program in accordance with 29CFR 1910.134
Below are a few of them that are required for use when working with Lead;
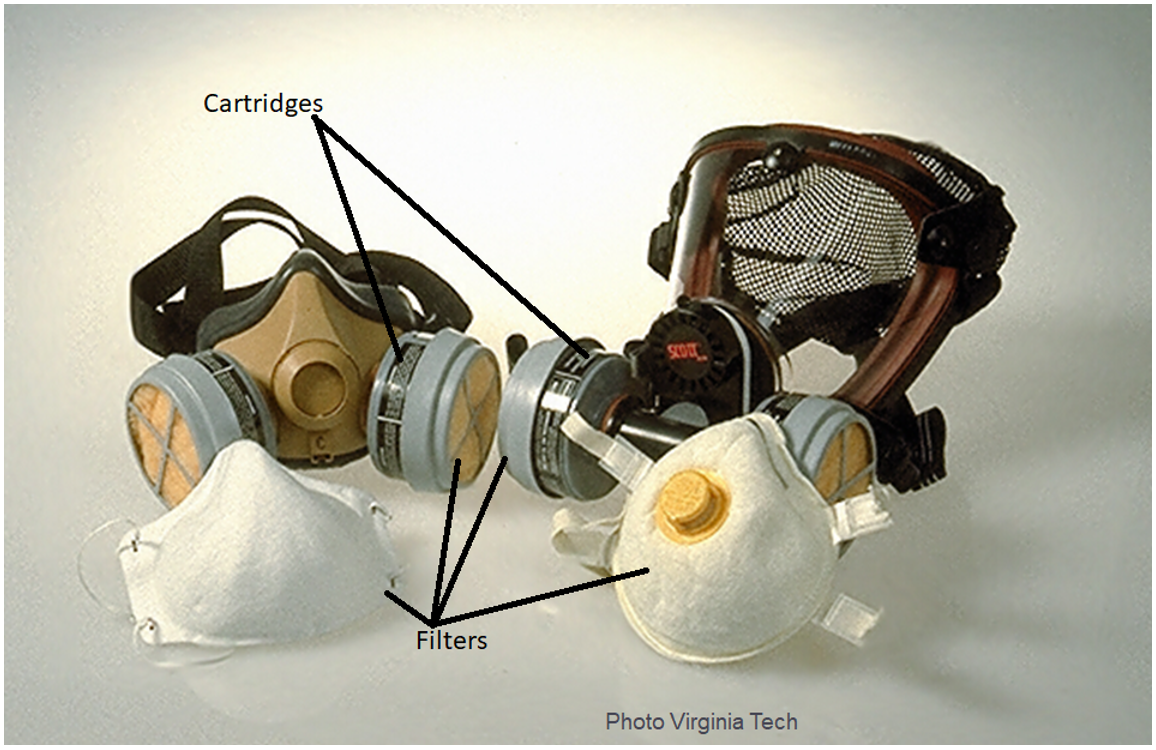
- Air-purifying respirators (APRs) work by removing gases, vapors, aerosols (droplets and solid particles), or a combination of contaminants from the air through the use of filters, cartridges, or canisters.
- A powered air-purifying respirator is a type of respirator used to safeguard workers against contaminated air. PAPRs consist of a headgear-and-fan assembly that takes ambient air contaminated with one or more type of pollutant or pathogen, actively removes a sufficient proportion of these hazards, and then delivers the clean air to the user’s face or mouth and nose. They have a higher assigned protection factor than filtering facepiece respirators such as N95 masks. PAPRs are sometimes called positive-pressure masks, blower units, or just blowers.
- A self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA), sometimes referred to as a compressed air breathing apparatus (CABA) or simply breathing apparatus (BA), isa device worn to provide breathable air in an atmosphere that is immediately dangerous to life or health.
- Supplied-Air Respirator Systems (SAR) utilize air from an external air source that is independent of the hazardous environment . These systems are great when extra comfort is important, adjustable airflows are required or have an extreme temperature application where a personal air-cooler or heater vastly improves the wearer’s comfort.
Up to 0.5 mg/m3:
(APF = 10) Any air-purifying respirator with an N100, R100, or P100 filter (including N100, R100, and P100 filtering facepieces) except quarter-mask respirators
Up to 1.25 mg/m3:
(APF = 25) Any supplied-air respirator operated in a continuous-flow mode
(APF = 25) Any powered, air-purifying respirator with a high-efficiency particulate filters
Up to 2.5 mg/m3:
(APF = 50) Any air-purifying, full-facepiece respirator with an N100, R100, or P100 filter.
(APF = 50) Any powered, air-purifying respirator with a tight-fitting facepiece and a high-efficiency particulate filter
(APF = 50) Any self-contained breathing apparatus with a full facepiece
(APF = 50) Any supplied-air respirator with a full facepiece
Up to 50 mg/m3:
(APF = 1000) Any supplied-air respirator operated in a pressure-demand or other positive-pressure mode
Up to 100 mg/m3
(APF = 2000) Any supplied-air respirator that has a full facepiece and is operated in a pressure-demand or other positive-pressure mode
Emergency or planned entry into unknown concentrations or IDLH conditions:
(APF = 10,000) Any self-contained breathing apparatus that has a full facepiece and is operated in a pressure-demand or other positive-pressure mode
(APF = 10,000) Any supplied-air respirator that has a full facepiece and is operated in a pressure-demand or other positive-pressure mode in combination with an auxiliary self-contained positive-pressure breathing apparatus
